
The product was used without further purification.Ĭonclusion. After the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, the solid residue was recovered by vacuum filtration. The reaction mixture was refluxed for 8h. Diethyl oxalate (30mL, 220 mmol) was added to the solution. 3,4-Diaminothiophene (2.85g, 25 mmol) was dissolved in 20mL of absolute ethanol. The following is a modification of previously reported methods. Procedure taken from p8534, of Journal of Organic Chemistry vol 73, 2008. After the aspirin was found pure, the melting point was taken. The ferric chloride test was performed to test the purity. The crystals were then weighed to calculate the percentage yield. The crystals were dried overnight on a watch glass. The crystals were removed and collected in a Hirsch funnel through vacuum filtration. Next, 3.0mL of water was added and stirred with a microspatula. The conical vial was placed into a small beaker and allowed to cool so that the acetylsalicylic acid would crystallize from the reaction mixture. The mixture was heated and stirred for 10 minutes and then allowed to cool.
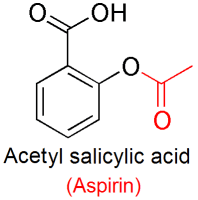

0.211g of dry salicylic acid was placed into a dry 5-mL conical vial, and dissolved in 0.480 mL of acetic anhydride and one drop of concentrated phosphoric acid in a hot water bath of 50 oC. A hypothesized recovery rater of above 50% was expected. The ferric chloride test and melting point were used to test the purity of the results. Synthesis of Acetylsalicylic Acid occurs by protonation of carbonyl (C=O) group, and a nucleophilic attack of OH on the acetic anhydride. This experiment was carried out to see how the hydroxyl group on the benzene ring in salicylic acid reacts with acetic anhydride to form an ester, and to make aspirin.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
